Friday, November 13, 2009
Turboprop Aircraft Engine
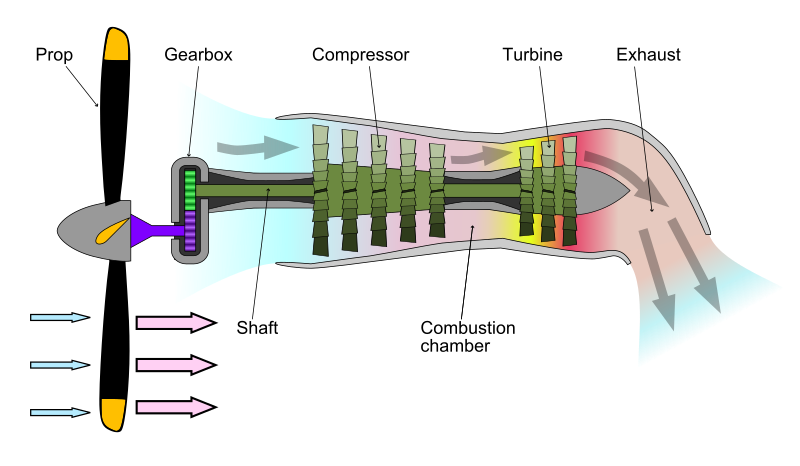
Turboprop engines are a type of aircraft powerplant that use a gas turbine to drive a propeller. The gas turbine is designed specifically for this application, with almost all of its output being used to drive the propeller. The engine's exhaust gases contain little energy compared to a jet engine and play a minor role in the propulsion of the aircraft.
The propeller is coupled to the turbine through a reduction gear that converts the high RPM, low torque output to low RPM, high torque. The propeller itself is normally a constant speed (variable pitch) type similar to that used with larger reciprocating aircraft engines.
Turboprop engines are generally used on small subsonic aircraft, but some aircraft outfitted with turboprops have cruising speeds in excess of 500 kt (926 km/h, 575 mph). Large military and civil aircraft, such as the Lockheed L-188 Electra and the Tupolev Tu-95, have also used turboprop power.
In its simplest form a turboprop consists of an intake, compressor, combustor, turbine, and a propelling nozzle. Air is drawn into the intake and compressed by the compressor. Fuel is then added to the compressed air in the combustor, where the fuel-air mixture then combusts. The hot combustion gases expand through the turbine. Some of the power generated by the turbine is used to drive the compressor. The rest is transmitted through the reduction gearing to the propeller. Further expansion of the gases occurs in the propelling nozzle, where the gases exhaust to atmospheric pressure. The propelling nozzle provides a relatively small proportion of the thrust generated by a turboprop.
Turboprops are very efficient at modest flight speeds (below 450 mph) because the jet velocity of the propeller (and exhaust) is relatively low. Due to the high price of turboprop engines they are mostly used where high-performance short-takeoff and landing (STOL) capability and efficiency at modest flight speeds are required. The most common application of turboprop engines in civilian aviation is in small commuter aircraft, where their greater reliability than reciprocating engines offsets their higher initial cost.
Source: Wikipedia
Labels:
aircraft engine,
airplane engine,
turbo engine
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
No comments:
Post a Comment